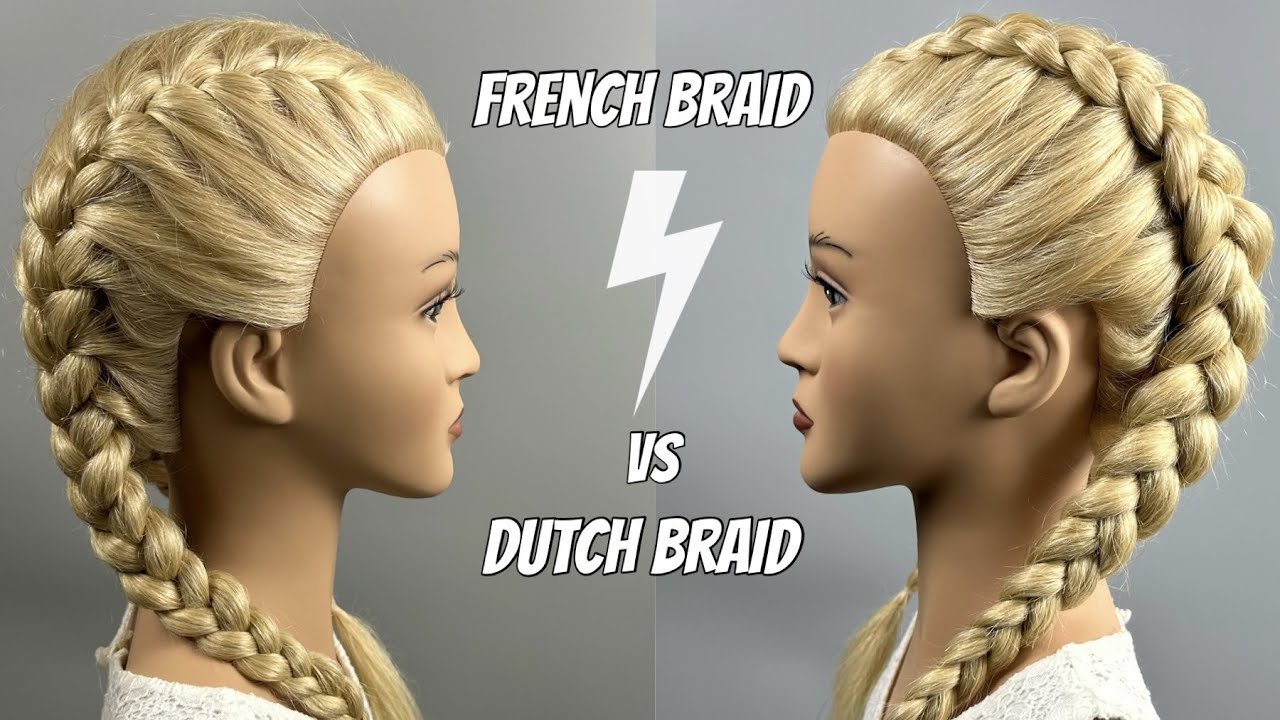
Are these two seemingly similar braids truly distinct? Understanding the differences between these popular styles can empower individuals to choose the best option for their needs.
Both braids involve intertwining strands of hair, but a key difference lies in the placement of the strands. A classic French braid, strands are interwoven under the base of the braid. In contrast, a Dutch braid features strands interwoven over the base of the braid, creating a distinctive appearance and a slightly different structure. This subtle difference in technique creates the visual distinction between the two. Visual examples can be found readily available online.
The choice between these two braids depends largely on personal preference and desired aesthetic. The visible "ridges" or "bumps" of the Dutch braid can contribute to a more textured or structured appearance. The tighter construction of a French braid might create a more smooth look. Both braids, though, serve the practical purpose of securing and styling hair, and can be easily modified and adjusted to suit individual preferences.
Moving forward, let's explore the intricacies of these braid styles in more detail, examining their adaptability, creative possibilities, and potential variations. Different methods exist for extending these basic styles, from intricate extensions to incorporating embellishments.
Dutch Braids vs. French Braids
Understanding the distinctions between Dutch and French braids is essential for achieving desired hairstyles. Both styles offer various applications, yet subtle differences in technique and outcome differentiate them.
- Placement (over/under)
- Texture (structured/smooth)
- Visual impact (ridged/flat)
- Hair handling (intertwining method)
- Styling versatility (variations)
- Hair type suitability (for different textures)
- Time commitment (complexity)
- Maintenance (durability)
The placement of strandsintertwined over or underis fundamental. A Dutch braid's "over" technique creates a visible ridge along the braid's length, impacting the hairstyle's texture and visual appeal. Conversely, the French braid's "under" method usually results in a flatter, smoother look. Versatility in styling involves variations like adding extensions or incorporating embellishments for both techniques. The choice hinges on desired aesthetics and the hair type; sleek styles may prefer French braids, while more texturized styles lean towards Dutch. Time commitment depends on the braid's intricacy. Ultimately, selection rests on understanding these key elements to tailor the style to one's preferences.
1. Placement (over/under)
The fundamental distinction between Dutch and French braids lies in the placement of the hair strands during the braiding process. This seemingly minor difference in technique significantly impacts the overall appearance and structure of the final braid. The "over" technique, characteristic of a Dutch braid, involves layering each strand over the braid's base, while the "under" technique, found in a French braid, interlaces each strand underneath the existing braid. This subtle difference in placement results in a distinct visual characteristic: Dutch braids often exhibit a ridge or raised texture along their length, in contrast to the generally smoother profile of French braids.
The practical significance of this distinction is considerable. A Dutch braid's raised structure offers a texturized, more voluminous aesthetic. This is particularly beneficial for those seeking a more pronounced, textured hairstyle. Conversely, the flatter profile of a French braid often lends itself better to a sleek, polished look, suiting individuals who prefer a more understated style. This understanding of the technical difference is critical for achieving a specific aesthetic and is important when discussing the practical applications of the various types of braids. Consider a situation where a performer needs a quick but stylish updo; the choice between a Dutch braid, providing noticeable texture, or a French braid, offering a smooth finish, becomes crucial to achieving the intended look. Different hair types and textures can also respond differently to these techniques; this consideration is fundamental for achieving the desired outcome. For example, thick hair may benefit from the slightly more structured hold of a Dutch braid.
In summary, the seemingly simple "over" versus "under" placement principle in braiding is the cornerstone of differentiating Dutch and French braids. The resulting visual and textural variations empower individuals to select the braid style that aligns with their desired aesthetic and hair type. Understanding this foundational difference is essential for mastering the technical aspects of braiding and achieving the desired outcome. This knowledge allows for adaptability in styling and achieving the look most suitable for the individual.
2. Texture (structured/smooth)
The contrasting textures achieved through Dutch and French braids are crucial considerations for selecting the appropriate style. The choice between a structured or smooth appearance directly impacts the overall aesthetic and suitability for various situations and hair types. Analyzing how each braid's technique affects the final texture provides insight into practical styling applications and individual preference.
- Dutch Braids and Structured Texture
The "over" technique of Dutch braiding, where strands are layered over the existing braid, inherently creates a textured look. This structure is often characterized by a visible ridge or "bump" effect, providing a pronounced, fuller, and more voluminous appearance. This texture is particularly suitable for styles aiming for a voluminous or texturized effect, like updos where a raised structure is desired. Examples include elaborate braided hairstyles, incorporating extensions to enhance the texture, or simply showcasing the braid's distinct raised structure. Furthermore, thicker or coarser hair types often benefit from the enhanced textural quality of a Dutch braid, as it can add definition to the hair's natural structure.
- French Braids and Smooth Texture
The "under" technique of French braiding, where strands are interwoven underneath the braid, usually results in a smoother, flatter finish. The interwoven strands tend to create a tightly bound, less textured appearance. This creates a polished, less pronounced look ideal for a sleek or casual style. Situations where a refined or sophisticated appearance is prioritized, such as formal events or occasions where a smooth hairstyle is desired, can benefit from the smooth profile of a French braid. Additionally, individuals with fine or straight hair types might find the smooth texture of a French braid more flattering than the potentially more prominent texture of a Dutch braid.
- Impact on Hair Type and Style
The choice between a structured or smooth texture in a braid is influenced by the characteristics of the hair itself. Coarser hair, for instance, can benefit from the additional volume and definition that the structured Dutch braid can provide, while finer hair may appear more polished and refined with the smooth texture of a French braid. The preferred style also impacts the choice of texture: a formal event may necessitate the sleek smoothness of a French braid, while a more casual setting might favor the structured texture of a Dutch braid.
- Versatility and Style Application
Understanding the connection between the braiding technique and resultant texture empowers individuals to choose a braid style that aligns with their desired aesthetic and hair type. The structured texture of a Dutch braid allows for a wider variety of stylistic embellishments, while the smoothness of a French braid enables a focus on sleek lines and a streamlined look. These choices can affect the overall look, from a simple everyday style to an elaborate, complex look, especially when considering the impact of the hairstyle in specific situations and settings.
In conclusion, the difference in texture between Dutch and French braids stems directly from their distinct braiding techniques. By considering these structural differences and their resultant textures, individuals can effectively choose the braid type that best complements their personal style, hair type, and desired aesthetic for any situation.
3. Visual Impact (ridged/flat)
The visual impact of a braid, categorized as either ridged or flat, arises directly from the fundamental difference in braiding technique between Dutch and French braids. The "over" technique of a Dutch braid, where hair strands are interlaced above the braid's base, results in a distinct ridge-like pattern along the braid's length. In contrast, the "under" technique of a French braid, wherein strands are woven underneath the base, generates a smoother, flatter appearance. This distinction in visual impact is a critical element in choosing between the two styles, as it significantly affects the overall aesthetic. A ridged Dutch braid projects a more voluminous and textured look, while a French braid offers a more streamlined, polished profile.
This visual distinction plays a significant role in various contexts. For instance, in formal settings, a French braid's smooth, polished appearance might be preferred, as it suggests a refined and composed style. In contrast, a Dutch braid's raised texture could be more appropriate for a casual or even theatrical event, where the visible structure contributes to a bold or pronounced look. Consider the practical application: a performer needing a striking updo may find the texture provided by a Dutch braid more advantageous than the smooth finish of a French braid. Further, the prominence of the ridges can also impact the perceived volume of the hair; the raised structure can visually add volume to thinner hair, while the smooth French braid might better suit hair with a fuller natural texture. Photographs and media examples demonstrating these visual distinctions are widely available, highlighting the impact of this technical difference on the final aesthetic.
Understanding the visual impactridged versus flatas a crucial element in differentiating Dutch and French braids is vital for both hairstylists and individuals seeking a specific look. The choice between a raised, textured braid or a sleek, streamlined braid depends on the desired aesthetic and the occasion. This understanding transcends mere aesthetics and impacts practical applications, guiding selections based on both personal preference and the context in which the hairstyle will be showcased.
4. Hair handling (intertwining method)
The method of intertwining hair strands is fundamental to distinguishing Dutch from French braids. Variations in this technique directly influence the visual outcome, structure, and overall aesthetic of the finished braid. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate style for a given purpose or hair type.
- Strand Overlap (Above vs. Below)
The core difference lies in the placement of each strand during the braiding process. A Dutch braid involves layering each strand over the existing braid. This "over" technique inherently creates a more pronounced texture and a raised, ridged appearance. In contrast, a French braid interlaces strands underneath the existing braid. The "under" technique generally produces a flatter, smoother texture, with a less visible structure. These opposing methods result in distinct visual outcomes, crucial for selecting the most appropriate style for a specific need.
- Strand Manipulation (Pulling and Weaving)
The handling of individual strands during the braiding process affects both the smoothness and volume of the finished braid. With a Dutch braid, strands are pulled somewhat more tightly against the scalp and woven over. This technique contributes to the structured texture. In a French braid, strands are incorporated more gently, often by weaving them under the base. This often results in a more flowing and polished style. This subtle difference in pulling and weaving is key to mastering the visual character of each braid.
- Tension and Volume (Tightness vs. Fluidity)
The tension applied during the braiding process directly influences the volume and final structure. Dutch braids often demand a tighter grip to maintain their pronounced ridge. Maintaining this tension during the braiding process affects the final volume. The French braid, due to its weaving under technique, may allow for more fluidity and less tension, resulting in a looser, less defined volume. This difference affects the overall style and its adaptability to different hair types and textures.
- Hair Direction and Positioning (Consistent vs. Intertwining)
Maintaining consistent direction and positioning of the strands affects the final structure of the braid. Dutch braids often have strands placed parallel and consistently against the scalp, contributing to the overall structured look. The French braid interweaves strands, allowing for a slightly more dynamic positioning. This difference impacts the final visual perception and the ability to incorporate various hair textures and directions effectively. The direction and positioning of the strands within the braid is a critical aspect of constructing the style and should be considered in the overall handling of the hair.
In conclusion, the distinct intertwining methods used in Dutch and French braids are not merely stylistic choices; they directly impact the texture, volume, and overall visual appeal of the finished hairstyle. The "over" versus "under" technique, combined with variations in strand manipulation and tension, results in characteristic differences that are key to understanding their visual impact and their suitability for various styling needs and hair types.
5. Styling versatility (variations)
The ability to adapt and modify Dutch and French braids offers significant versatility in hairstyling. Exploring variations in these foundational braid types allows for a broad spectrum of stylistic outcomes, ranging from simple everyday styles to elaborate elaborate updos. This adaptability is critical in tailoring hairstyles to individual preferences, hair types, and specific situations.
- Extensions and Embellishments
Both Dutch and French braids readily accommodate extensions and embellishments. Adding braids, ribbons, beads, or other decorative elements transforms the basic style into a more elaborate or visually captivating design. This versatility is crucial for special occasions or events requiring a more dramatic or intricate hairstyle. The structured texture of a Dutch braid might lend itself well to bold embellishments, while the smoothness of a French braid often complements more subtle additions. Practical application demonstrates the adaptability of each style.
- Complexity and Intricacy
Variations in the braiding technique allow for increasing levels of complexity and intricacy. Basic Dutch and French braids can be easily modified to create more intricate patterns, such as fishtail or other complex braid elements incorporated into the core structure. This capacity for evolving from a simple style to a highly detailed design demonstrates the versatility of both styles. The choice of complexity often depends on factors like time constraints, desired level of detail, and the desired overall look.
- Adaptation to Hair Type
The adaptability of these braids to different hair types is evident in variations. Adjusting tension and incorporating appropriate hair-type-specific techniques allows for adapting a basic style to suit various textures, thicknesses, and lengths of hair. For example, Dutch braids might be better suited for coarse or thick hair due to the structure of the braid, while French braids can be adapted for finer or more delicate hair. The variations reflect the fundamental necessity for braids to complement diverse hair characteristics.
- Modifications for Specific Styles
These braids easily adapt to create a variety of specific hairstyles. Modifications like adding twists, adding sections, and altering the direction of the braids allow for a wide spectrum of outcomes. This significant adaptability provides a range of styles suitable for different hair lengths and aesthetic preferences. The variations in the method of styling, from loose braids to tightly woven updos, contribute to the versatile nature of these braid styles, which are capable of adapting to various demands and expectations for different occasions.
In conclusion, the demonstrable versatility of Dutch and French braids extends well beyond basic structures. From incorporating embellishments to adjusting techniques for diverse hair types, these variations highlight the adaptability and practicality of these braids in diverse situations and aesthetics. This adaptability further underscores the significance of understanding the fundamentals of each style to achieve the desired outcome. The range of potential styles showcases the essential role of versatility in hairstyling and makes both Dutch and French braids valuable choices for various occasions and personal preferences.
6. Hair type suitability (for different textures)
The suitability of Dutch and French braids for various hair types is a crucial aspect of selecting the most appropriate style. Hair texture, thickness, and length all interact with the braiding techniques, influencing the final appearance and manageability of the style. Understanding these interactions is vital for achieving a successful and comfortable result.
Different hair types respond differently to the distinct techniques of Dutch and French braids. Coarse or thick hair often benefits from the structured, slightly more raised texture of a Dutch braid, which can provide additional volume and hold. The tighter weaving inherent in the Dutch technique may also be more effective in securing and controlling thick or coarse strands. Conversely, fine or thin hair may appear more manageable and less weighed down with the smoother, generally flatter profile of a French braid. The less pronounced structure of a French braid may create a lighter look that avoids overwhelming the overall volume of finer hair. Additionally, hair length plays a role. A Dutch braid may be more visually impactful on long or medium-length hair due to the distinct ridge. Shorter hair may benefit from a French braid's streamlined appearance.Hair porosity also influences choice. Hair that absorbs moisture readily may have its texture more prominently displayed by the pronounced texture of the Dutch braid, while less porous hair might look more polished and streamlined with the French braid.Examples of these practical considerations include: a stylist choosing a French braid for a client with fine, easily flattened hair to achieve a sleek look; or a Dutch braid chosen for a client with thick, coarse hair to accentuate volume and create a textured updo.
Ultimately, understanding hair type suitability is paramount for selecting the ideal braid style. Choosing a braid that complements hair characteristics leads to a more pleasing, secure, and comfortable hairstyle. By understanding how different braiding techniques interact with various hair types, individuals can make informed choices for achieving the desired aesthetic and maintaining a healthy and well-maintained hairstyle, whether for daily wear or special occasions.
7. Time Commitment (Complexity)
The time required to execute a Dutch braid versus a French braid is a significant consideration, influenced by the fundamental difference in braiding techniques. The complexity of each style correlates directly with the execution time. A Dutch braid, characterized by the "over" method of weaving, often necessitates more deliberate strand manipulation to achieve the distinctive raised texture. This meticulous layering typically translates to a longer execution time compared to the "under" technique employed in a French braid. The intricacies of maintaining the raised ridges and consistent placement increase the time commitment. The varying degrees of tension required to achieve the desired visual effect also impact the time needed for execution.
Practical applications highlight the importance of time considerations. A quick updo for a casual event might lean toward a simpler French braid, due to its relatively faster execution time. On the other hand, a more intricate, textured hairstyle, such as a Dutch braid incorporated with decorative elements, will inevitably require a longer time commitment. A hairstylist working with a client who has a specific time constraint would need to consider the practical implications of the chosen braid style. Conversely, for a client with ample time and a desire for a meticulously detailed hairstyle, the added time commitment of a Dutch braid might be advantageous. In scenarios like wedding preparations or formal events where time management is crucial, the quicker execution of a French braid becomes a more practical option, especially for individuals with complex hair requirements.
Recognizing the relationship between braiding techniques and time commitment is critical for both stylists and individuals. Accurate time estimations are vital for appointment scheduling and ensuring a satisfying experience for all parties. Understanding the nuances of braid complexity allows for informed decision-making, enabling both the client and the stylist to set realistic expectations. This knowledge becomes even more pertinent in scenarios involving intricate styles, ensuring that the chosen hairstyle aligns with available time constraints. Ultimately, making this connection underscores the practical significance of considering both the aesthetic and the operational aspects of various braiding styles.
8. Maintenance (durability)
Evaluating the durability of Dutch and French braids is crucial for selecting the appropriate style, particularly considering the time commitment and desired longevity of the hairstyle. Differences in the braiding techniques directly influence how long the style holds its shape and form, and factors like hair type and daily activities further shape the maintenance needs. Understanding these factors is vital for informed choices about both daily care and the overall success of the style.
- Tension and Tightness of Intertwining
The braiding technique's tension significantly affects the braid's longevity. Dutch braids, with their characteristic "over" weave, often require tighter intertwining to maintain the raised ridges and distinct texture. This tighter structure, while potentially providing greater initial hold, might also lead to increased stress on the hair strands, potentially contributing to quicker breakage if not properly cared for. Conversely, the "under" weaving of French braids usually involves less tension, leading to a potentially looser and more flexible braid structure, potentially enhancing durability. This is particularly significant for individuals with fine hair, where excessive tension could lead to damage. Practical examples include braids that need daily adjustments to avoid loosening, and others that require more maintenance to prevent tangles and breakage.
- Hair Type and Texture Influence
Hair type and texture greatly influence the durability of any hairstyle, including braids. Coarse or thick hair often requires stronger hold and potentially more time-consuming maintenance to maintain a braid's integrity. In such instances, the added structure of a Dutch braid might prove advantageous in maintaining the style's integrity for a longer period. Fine or thin hair, however, might be better suited for the less demanding structure of a French braid, which may experience less stress and hold its shape for a longer time due to less tension on the individual strands. Practical considerations include hairstyles for different hair types, recognizing the need for extra care with thicker hair and potential issues with thinner hair that is vulnerable to damage.
- Activity Level and Environmental Factors
Everyday activities and environmental factors impact a braid's durability. Individuals leading active lifestyles or those exposed to frequent friction or moisture may experience more rapid loosening or damage to either style of braid. Rougher activities might cause increased wear on the braid, potentially leading to tangles and loosening faster. Environmental factors such as humidity or exposure to direct sunlight might also play a role in the durability of the braid. Consider an individual with a physically demanding job or someone living in a very humid climate; the choice of braid style will affect the rate of maintenance and the style's overall duration. Practical examples include braids failing quickly in highly active individuals, those who engage in frequent physical activities, and those living in climates with high humidity or strong sunlight.
- Maintenance Practices and Daily Care
Regular maintenance practices, such as gentle detangling, appropriate hair products, and careful handling, can significantly enhance the lifespan of any braid style. Using products that hydrate hair can reduce stress on individual strands. Furthermore, minimizing friction and tangles by using hair accessories or securing the braid correctly will directly impact longevity. Consistent care routines and understanding of hair type help in ensuring a more durable and longer-lasting style. Practical implications include using gentle techniques for detangling, choosing suitable hair products to minimize breakage, and understanding the need for extra care depending on hair texture and daily activities.
Ultimately, the durability of Dutch and French braids is a function of several interacting factors. Considering the tension and tightness of the weave, hair type, activity levels, and consistent care practices empowers individuals to choose a braid style best suited to their needs and lifestyle, ensuring the desired style holds its shape throughout its intended lifespan.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the distinctions between Dutch and French braids. Clarifying these differences empowers individuals to select the most appropriate style for their needs and preferences.
Question 1: What is the primary difference between a Dutch braid and a French braid?
The fundamental distinction lies in the placement of strands. A French braid weaves strands under the existing braid, whereas a Dutch braid interlaces strands over the base. This seemingly minor difference creates distinct visual and textural characteristics.
Question 2: How do these different weaving techniques affect the overall appearance?
The "over" technique of a Dutch braid typically results in a more textured, ridged, or voluminous look. The "under" technique of a French braid usually produces a smoother, flatter finish. This visual contrast is crucial for selecting the appropriate style based on desired aesthetic.
Question 3: Which braid type is better suited for different hair types?
Thick or coarse hair might find the structure of a Dutch braid more supportive and volumizing. Fine or thin hair often benefits from the smoother, potentially less overwhelming texture of a French braid. Hair length and porosity also play a role in suitability.
Question 4: Does the complexity of the braid affect the time needed for execution?
Generally, Dutch braids, due to the "over" weaving and maintaining ridges, require more time to execute compared to French braids. The increased intricacy in Dutch braid construction leads to a longer overall execution time. The desired level of detail impacts the total time needed.
Question 5: How does the style's longevity vary between Dutch and French braids?
Factors like hair type and activity level influence the durability of both styles. Dutch braids, often with tighter weaves, may hold their shape longer, while French braids, with a less demanding structure, can sometimes maintain a desired form for a shorter duration. Daily maintenance and environmental conditions can also influence longevity.
Understanding these distinctions enables individuals to make informed decisions when selecting a braid style that aligns with personal preferences, hair type, and desired aesthetic outcomes.
This concludes the Frequently Asked Questions. The next section will explore the practical applications and styling possibilities of these braid types in more depth.
Conclusion
This exploration of Dutch and French braids reveals significant distinctions stemming from fundamental differences in braiding technique. The "over" weaving of a Dutch braid results in a structured, often ridged appearance, offering volume and texture. Conversely, the "under" weaving of a French braid typically creates a smoother, flatter look. These visual distinctions are crucial in selecting the appropriate style for various hair types, desired aesthetics, and specific situations. Considerations of hair type, activity levels, and maintenance requirements further inform the choice between these two popular braid styles. Time commitment also varies, with Dutch braids often demanding more time for execution. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of these techniques empowers individuals and stylists to make informed choices that optimize the durability and visual impact of the desired hairstyle.
The choice between a Dutch or French braid transcends mere aesthetics; it reflects a deeper understanding of how specific braiding techniques interact with individual hair characteristics and desired outcomes. This knowledge extends beyond personal preference, influencing decisions in various contexts, from everyday styling to formal events. By recognizing the intricacies of these two braid types, individuals and stylists can tailor hairstyles to best suit the individual, the occasion, and the desired aesthetic. Future exploration might examine variations, extensions, and further specific applications of these styles in diverse hair contexts.
You Might Also Like
Stunning Egyptian Tattoo Designs: 100+ Ideas & InspirationCelebrating 1 Year: Relationship Milestones & Advice
Johnny Mathis: Timeless Hits & Iconic Vocals
Ancient Pick-Up Lines: The Oldest & Funniest
Ocean-Inspired Names: Unique & Beautiful Baby Names
Article Recommendations