Introduction to Ecological Succession
Ecological succession is a fascinating natural process that describes the gradual and often predictable changes in the composition and structure of an ecological community over time. It is a fundamental concept in ecology, illustrating how ecosystems evolve in response to disturbances and environmental changes. In 2024, as we become increasingly aware of environmental issues and the need for conservation, understanding ecological succession is more important than ever. This process not only helps us comprehend how ecosystems recover from disruptions, such as fires or hurricanes, but also provides insight into how we can support biodiversity and promote ecological resilience.
Types of Ecological Succession
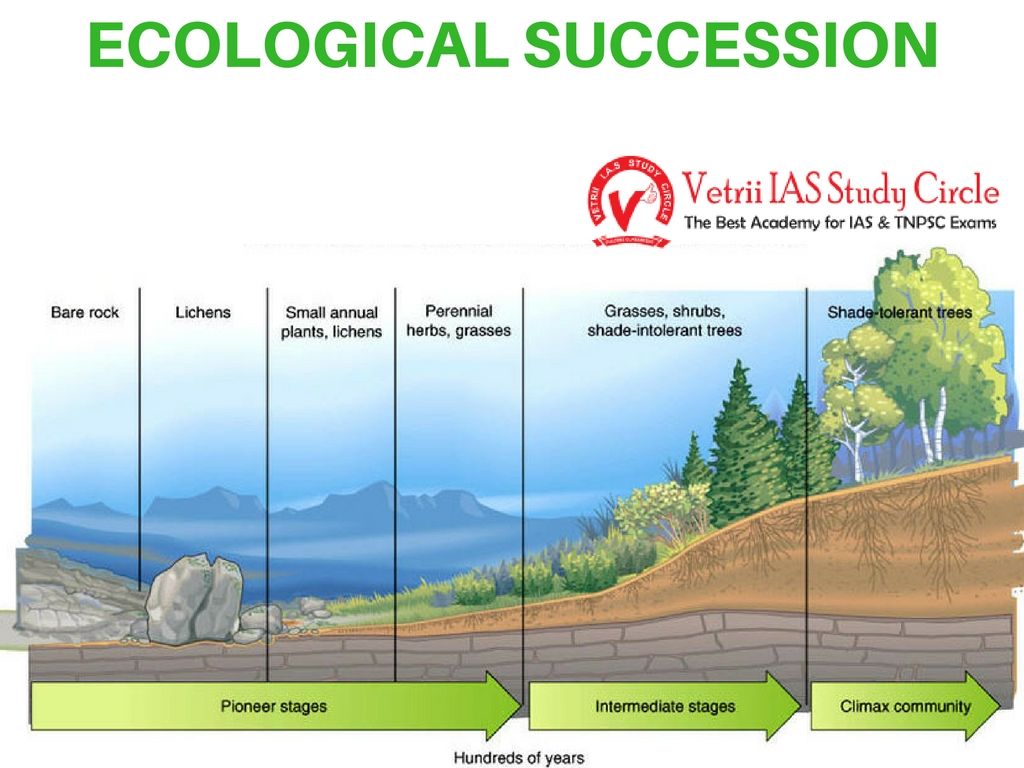
There are two primary types of ecological succession: primary and secondary. Primary succession occurs in lifeless areas where there is no soil, such as on bare rock after a volcanic eruption or on sand dunes. This type of succession begins with pioneer species, like lichens and mosses, that can survive in such harsh conditions and gradually create a more hospitable environment for other species. Secondary succession, on the other hand, takes place in areas where an existing community has been disturbed but soil and some organisms still remain. Events like forest fires, floods, or human activities can trigger secondary succession. Understanding these types helps ecologists predict how ecosystems might change and recover over time.
The Role of Pioneer Species
Pioneer species play a crucial role in the ecological succession process. These hardy organisms are the first to colonize a barren or disturbed environment. Due to their unique adaptations, pioneer species can withstand harsh conditions and initiate ecological recovery. They are vital because they modify the environment, making it more suitable for subsequent species to thrive. For example, lichens and mosses in primary succession can break down rocks and accumulate organic matter, eventually leading to soil formation. This transformation paves the way for other plants, insects, and animals to establish themselves, thereby increasing biodiversity and ecosystem complexity over time.
Read also:Jimmie Walkers Net Worth Behind His Financial Success
Stages of Ecological Succession
Ecological succession typically progresses through several stages, each characterized by distinct species compositions and interactions. In primary succession, the initial stage involves the colonization by pioneer species, followed by the establishment of grasses and herbaceous plants. As soil quality improves, shrubs and small trees begin to appear, leading to the development of a more complex community. Finally, a climax community forms, which is a stable and mature ecosystem. In secondary succession, the process is similar but generally faster, as the soil and seed bank are already present. Understanding these stages helps ecologists and conservationists monitor ecosystem recovery and manage natural resources more effectively.
Factors Influencing Ecological Succession
Various factors influence the rate and trajectory of ecological succession. Abiotic factors, such as climate, soil type, and topography, play a significant role in determining which species can establish and thrive. Biotic factors, including the presence of existing organisms, competition, and symbiotic relationships, also impact succession dynamics. Additionally, disturbances like fires, storms, and human activities can alter succession pathways. By understanding these factors, ecologists can predict how ecosystems will respond to changes and implement strategies to promote ecological resilience and biodiversity conservation. In 2024, with the increasing frequency of climate-related disturbances, this knowledge is crucial for sustainable ecosystem management.
The Importance of Biodiversity in Succession
Biodiversity is a key component of ecological succession. As succession progresses, species diversity typically increases, leading to more complex and stable ecosystems. High biodiversity enhances ecosystem functions, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and pest control, contributing to overall ecological health. In 2024, preserving biodiversity is a global priority, as it supports ecosystem resilience in the face of environmental changes and human impacts. By understanding ecological succession, we can develop conservation strategies that maintain or restore biodiversity, ensuring the continued provision of ecosystem services and the survival of diverse species in a rapidly changing world.
Human Impacts on Ecological Succession
Human activities have a profound impact on ecological succession. Land-use changes, pollution, and climate change are some of the major factors altering natural succession patterns. Urbanization and agriculture often lead to habitat fragmentation and loss, disrupting succession processes and reducing biodiversity. Climate change, with its associated shifts in temperature and precipitation, can alter the timing and progression of succession, affecting species distributions and ecosystem stability. In 2024, mitigating these impacts requires a concerted effort to adopt sustainable practices, such as habitat restoration and conservation planning, to support natural succession and promote ecological resilience.
Ecological Succession and Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant challenge to ecological succession, altering the conditions and processes that drive ecosystem recovery and development. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events can disrupt succession pathways, leading to shifts in species composition and distribution. Some species may struggle to adapt to new conditions, while others may thrive, potentially leading to invasive species outbreaks. In 2024, understanding the interactions between ecological succession and climate change is crucial for predicting future ecosystem dynamics and developing adaptive management strategies. By promoting resilience through conservation and restoration efforts, we can help ecosystems withstand and recover from climate-related disturbances.
Restoration Ecology and Succession
Restoration ecology is a field dedicated to restoring degraded ecosystems to their natural states, and ecological succession plays a central role in these efforts. By harnessing the principles of succession, restoration ecologists can design interventions that accelerate ecosystem recovery and enhance biodiversity. Techniques such as reforestation, soil amendment, and the reintroduction of native species can help guide succession towards desired outcomes. In 2024, as the need for ecosystem restoration grows, understanding ecological succession is essential for developing effective strategies that promote sustainable land management and biodiversity conservation. Through restoration, we can repair the damage caused by human activities and ensure the long-term health of our planet.
Read also:A Look Into The Bond Between Kim Porter And Tupac
Conclusion: Embracing Ecological Succession for a Sustainable Future
Ecological succession is a powerful process that illustrates the dynamic nature of ecosystems and their capacity for recovery and adaptation. As we face unprecedented environmental challenges in 2024, understanding and embracing ecological succession is crucial for achieving a sustainable future. By recognizing the importance of succession in ecosystem management, we can develop strategies that support biodiversity, enhance resilience, and mitigate the impacts of human activities and climate change. Whether through conservation, restoration, or sustainable development, integrating the principles of ecological succession into our actions will help preserve the natural world for future generations.