Introduction to Beta Decay
Beta decay is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in the field of nuclear physics. It involves the transformation of a neutron into a proton or vice versa, accompanied by the emission of a beta particle, which is either an electron or a positron. This process is fundamental in understanding the stability of atomic nuclei and the behavior of radioactive elements. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of beta decay, exploring its types, mechanisms, and significance in both natural and artificial contexts. Whether you're a student, a science enthusiast, or someone curious about the atomic world, this guide aims to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of beta decay in relaxed, easy-to-understand language.
The Basics of Beta Decay
At its core, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay involving the weak nuclear force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature. Unlike alpha decay, which is characterized by the emission of helium nuclei, beta decay involves the emission of beta particles. These particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons. The process occurs in unstable nuclei where the neutron-to-proton ratio is not optimal, prompting the nucleus to undergo decay in an attempt to reach a more stable state. Beta decay can occur in two forms: beta-minus (β-) decay and beta-plus (β+) decay. Each form has distinct characteristics and implications, which we'll explore in the following sections.
Beta-Minus Decay: The Electron Emission
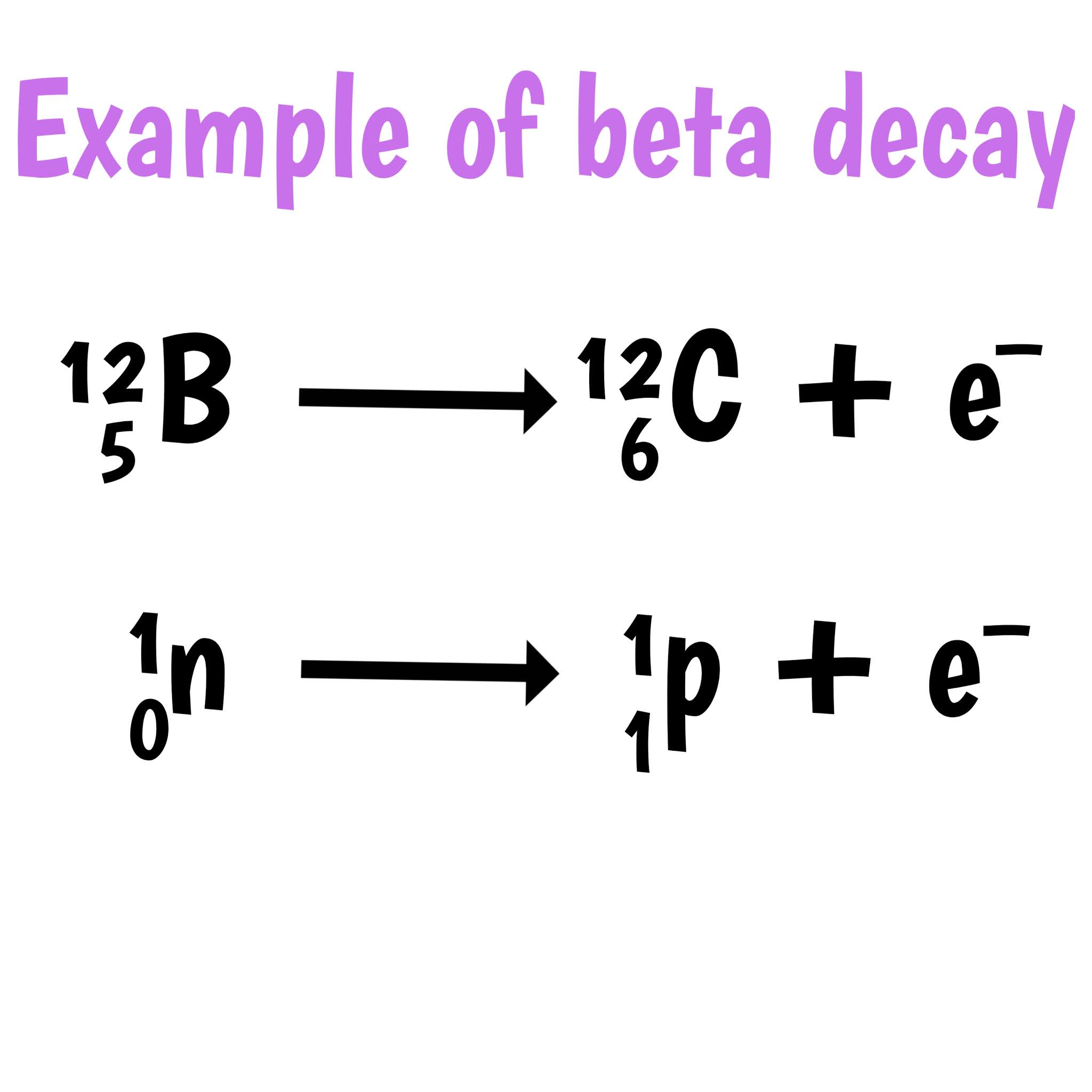
Beta-minus decay is a type of beta decay where a neutron in an unstable nucleus is transformed into a proton, emitting an electron (beta particle) and an antineutrino. This process increases the atomic number of the element by one, effectively changing it into a different element. For instance, carbon-14 undergoes beta-minus decay to form nitrogen-14. This decay is commonly observed in isotopes with an excess of neutrons. The emitted electron, being negatively charged, carries away kinetic energy, while the antineutrino, a nearly massless particle, also takes away energy, helping to conserve energy and momentum in the decay process. Understanding beta-minus decay is crucial for applications in carbon dating and nuclear energy.
Read also:The Newest Dairy Queen Blizzard Of The Month A Sweet Treat You Wont Want To Miss
Beta-Plus Decay: The Positron Emission
In contrast to beta-minus decay, beta-plus decay occurs when a proton in an unstable nucleus is converted into a neutron, releasing a positron and a neutrino. This process decreases the atomic number by one, transforming the element into a different one. An example of beta-plus decay is the transformation of carbon-11 into boron-11. Beta-plus decay is less common than beta-minus decay and typically occurs in proton-rich nuclei. The emitted positron, being the antimatter counterpart of the electron, eventually encounters an electron, leading to annihilation and the production of gamma rays. This form of decay is instrumental in medical imaging techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET scans).
Neutrinos and Antineutrinos: The Ghost Particles
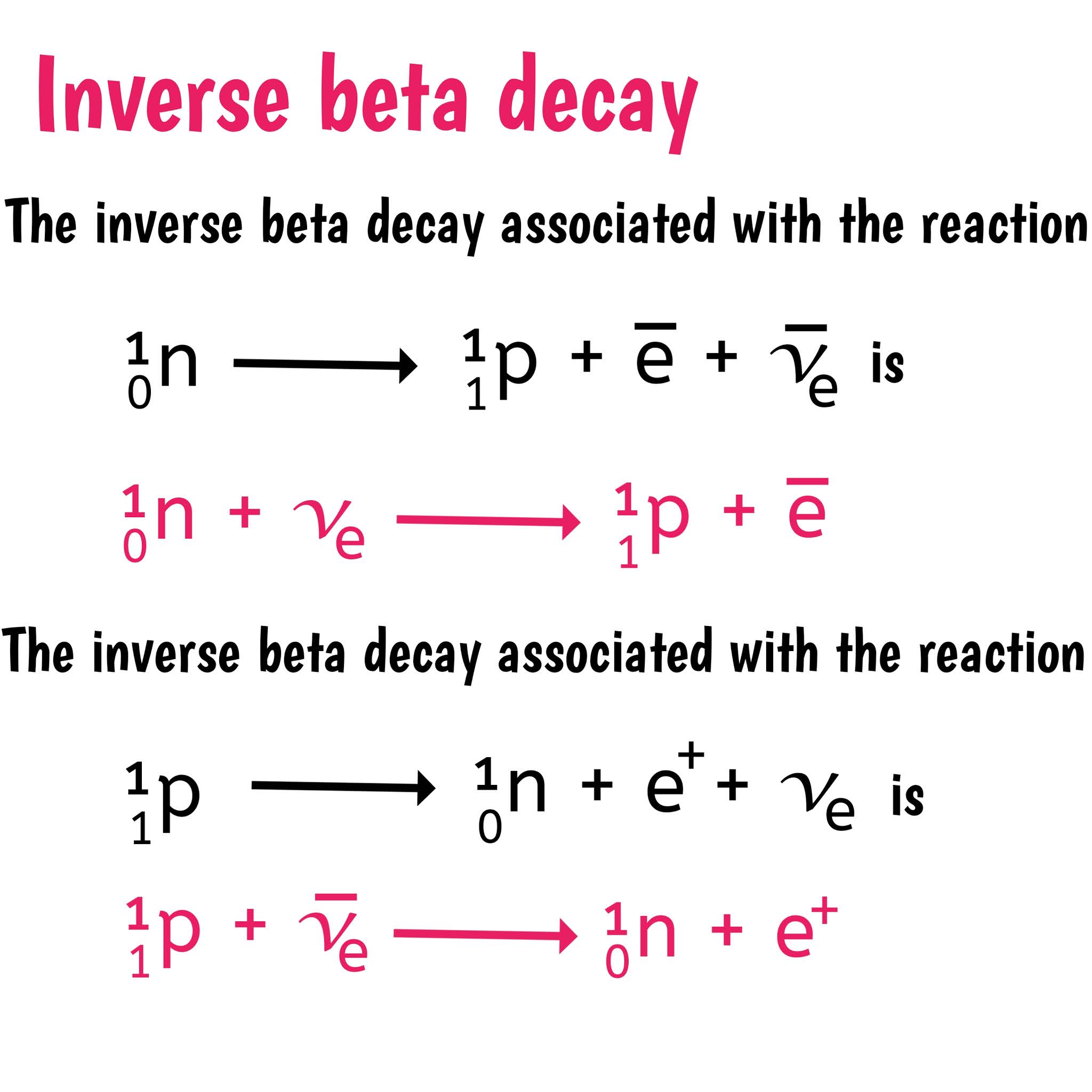
Neutrinos and antineutrinos are elusive particles that play a critical role in beta decay. These particles are incredibly difficult to detect due to their weak interaction with matter. They are neutral, nearly massless, and travel at speeds close to that of light. In beta-minus decay, an antineutrino is emitted, while in beta-plus decay, a neutrino is produced. These particles help conserve the fundamental laws of physics, such as the conservation of energy, momentum, and angular momentum during the decay process. Despite being nearly undetectable, neutrinos and antineutrinos are crucial for our understanding of the universe, providing insights into processes occurring in stars and the fundamental nature of matter.
The Role of Beta Decay in Nature
Beta decay is not just a laboratory phenomenon; it is a natural process that occurs throughout the universe. In stars, beta decay plays a pivotal role in the synthesis of elements during nuclear reactions. It is also responsible for the natural radioactivity observed in certain isotopes on Earth. For example, potassium-40, a naturally occurring isotope, undergoes beta decay, contributing to the natural background radiation we experience daily. Furthermore, beta decay is instrumental in the formation of isotopes used in radiometric dating techniques, allowing scientists to determine the age of rocks, fossils, and archaeological artifacts. This natural process is a key component of the cosmic cycle, helping to create and transform elements over time.
Applications of Beta Decay in Technology
Beyond its natural occurrence, beta decay has significant applications in technology and industry. One of the most notable applications is in the field of medicine, particularly in diagnostic imaging. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans, which utilize the principles of beta-plus decay, are used to detect cancer and monitor brain activity. In the energy sector, beta decay is harnessed in certain types of nuclear reactors and batteries, providing a long-lasting power source for spacecraft and remote sensing equipment. Additionally, beta decay is used in quality control processes, such as thickness gauging and material analysis. These applications underscore the importance of beta decay in advancing technology and improving quality of life.
Beta Decay and the Weak Nuclear Force
The weak nuclear force, responsible for beta decay, is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, alongside gravity, electromagnetism, and the strong nuclear force. It is unique in that it allows for the transformation of one type of subatomic particle into another, such as a neutron into a proton. The weak force is mediated by the exchange of W and Z bosons, which are much heavier than protons and neutrons, leading to the short range of the force. Despite its name, the weak nuclear force is a powerful mechanism that governs the processes of beta decay and plays a crucial role in the evolution of stars and the universe. Understanding this force is essential for physicists seeking to unravel the mysteries of the atomic world.
Challenges in Studying Beta Decay
While beta decay is a well-established concept in physics, studying and understanding it presents several challenges. The detection of neutrinos and antineutrinos, key particles in the decay process, is notoriously difficult due to their weak interaction with matter. Advanced detectors and experimental setups are required to capture these elusive particles, often involving massive underground facilities shielded from cosmic radiation. Additionally, theoretical models of beta decay must account for various factors, including nuclear structure and particle interactions, making accurate predictions complex. Despite these challenges, ongoing research and technological advancements continue to enhance our understanding of beta decay, contributing to the broader field of particle physics.
Read also:Jimmie Walkers Net Worth Behind His Financial Success
Conclusion: The Future of Beta Decay Research
As we move into 2024 and beyond, the study of beta decay remains a vibrant and evolving field of research. Scientists continue to explore the fundamental aspects of this process, seeking to refine theoretical models, improve detection methods, and uncover new applications. The insights gained from studying beta decay have far-reaching implications, from enhancing our understanding of the universe to developing advanced technologies. As our knowledge of beta decay expands, we can expect to see new breakthroughs that will further illuminate the mysteries of the atomic world and its role in the cosmos. Whether through academic research, practical applications, or technological innovations, beta decay continues to be a cornerstone of modern science.