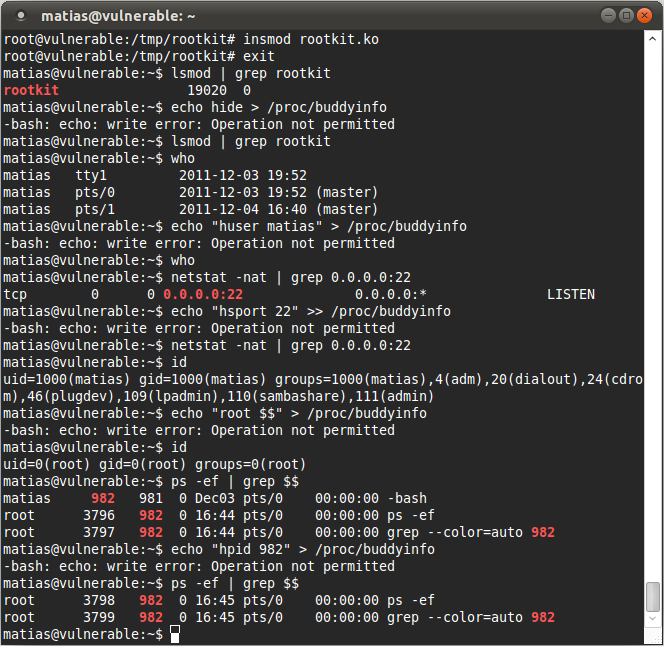
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the term "linux rootkit" has become synonymous with stealthy, malicious software that poses significant threats to Linux-based systems. A linux rootkit is designed to gain unauthorized access, conceal its presence, and often facilitate further exploitation of a system. For system administrators and cybersecurity professionals, understanding how these rootkits operate is critical in mitigating their impact and fortifying system defenses.
What makes linux rootkits particularly alarming is their ability to blend seamlessly with a system's legitimate processes, making detection a daunting task. Rootkits are not inherently harmful by themselves, but their primary function is to provide a platform for malicious activities such as data theft, privilege escalation, and the installation of additional malware. With the proliferation of Linux servers in enterprise environments, the stakes have never been higher for detecting and preventing these sophisticated threats.
This article delves deep into the intricate workings of linux rootkits, exploring their types, methods of deployment, and the countermeasures that can be implemented to safeguard systems. Whether you're a seasoned IT professional, a cybersecurity enthusiast, or someone simply curious about the threats lurking in the digital shadows, this guide will arm you with the knowledge to better understand and combat linux rootkits effectively.
Read also:Jimmie Walkers Net Worth Behind His Financial Success
Table of Contents
- What is a Linux Rootkit?
- Types of Linux Rootkits
- How Linux Rootkits Operate
- Common Techniques Used by Rootkits
- Real-World Examples of Linux Rootkits
- Signs Your System May Be Infected
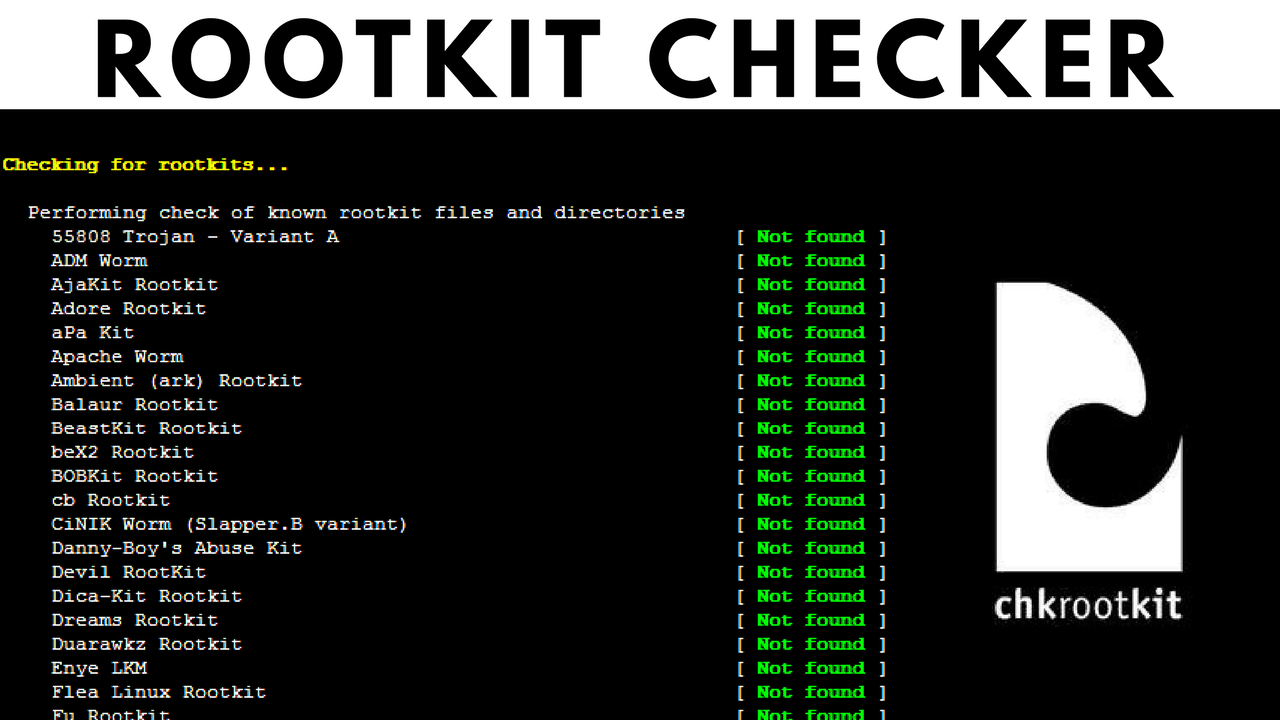
- How to Detect Linux Rootkits
- Tools for Rootkit Detection
- Removing and Remediating Linux Rootkits
- Preventing Linux Rootkit Infections
- Linux Rootkits and Cybersecurity
- Legal and Ethical Implications
- Challenges in Dealing with Rootkits
- Future Trends in Rootkit Development
- Frequently Asked Questions